목차
- 이진 트리 란?
- 이진 트리의 특징
- 이진 트리 예시
- 이진 트리 구현
- 이진 트리 응용(트리 복원)
- 트리 문제(BOJ)
이진 트리(Binary Tree) 란?
- 이진 트리는 가장 많이 사용되는 비선형 자료구조 이다.
- 이진 트리는 데이터의 탐색 속도 증진 을 위해 사용하는 구조이다.
이진 트리(Binary Tree)의 특징
- 힙 정렬(Heap Sort)을 구현할 때 이진 트리를 이용하여 구현할 수 있다.
- 이진 트리에서 데이터를 탐색 하는 방법은 크게 세 가지 방법이 있다.
- 전위 순회 (Preorder Traversal)
- 자기 자신을 먼저 처리한다.
- 왼쪽 자식을 방문.
- 오른쪽 자식을 방문
- 중위 순회 (Inorder Traversal)
- 왼쪽 자식을 방문.
- 자기 자신을 먼저 처리한다.
- 오른쪽 자식을 방문
- 후위 순회 (Postorder Traversal)
- 왼쪽 자식을 방문
- 오른쪽 자식을 방문.
- 자기 자신을 먼저 처리한다.
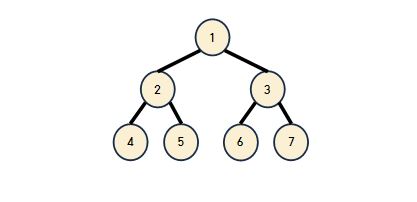
- 이진트리(Binary Tree) 형태
- 전위 순회 (Preorder Traversal)
- 자기 자신을 먼저 처리한다.
- 왼쪽 자식을 방문.
- 오른쪽 자식을 방문
- 중위 순회 (Inorder Traversal)
- 왼쪽 자식을 방문.
- 자기 자신을 먼저 처리한다.
- 오른쪽 자식을 방문
- 후위 순회 (Postorder Traversal)
- 왼쪽 자식을 방문
- 오른쪽 자식을 방문.
- 자기 자신을 먼저 처리한다.
이진 트리(Binary Tree)의 알고리즘 예시
- 전위 순회 (Preorder Traversal) 1 - 2 - 4 - 5 - 3 - 6 - 7
- 중위 순회 (Inorder Traversal) 4 - 2 - 5 - 1 - 6 - 3 - 7
- 후위 순회 (Postorder Traversal) 4 - 5 - 2 - 6 - 7 - 3 - 1
이진 트리(Binary Tree) C++ 구현
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int num = 15;
// 하나의 노드 정보를 선언한다.
typedef struct node *treePointer;
typedef struct node {
int data;
treePointer leftChild, rightChild;
} node;
// 중위 순회
void inorder(treePointer ptr){
if(ptr){
inorder(ptr->leftChild);
cout << ptr->data << ' ';
inorder(ptr->rightChild);
}
}
// 전위 순회
void preorder(treePointer ptr){
if(ptr){
cout << ptr->data << ' ';
preorder(ptr->leftChild);
preorder(ptr->rightChild);
}
}
//후위 순회
void postorder(treePointer ptr){
if(ptr){
postorder(ptr->leftChild);
postorder(ptr->rightChild);
cout << ptr->data << ' ';
}
}
int main(void){
// 데이터가 들어갈 배열을 생성
node nodes[num + 1];
// 각 원소를 초기화
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++){
nodes[i].data = i;
nodes[i].leftChild = NULL;
nodes[i].rightChild = NULL;
}
// 각 노드를 연결해준다.
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++){
// 2의 배수라면 짝수라면 왼쪽에 넣어준다.
if(i % 2 == 0){
nodes[i / 2].leftChild = &nodes[i];
}
// 홀수라면 오른쪽에 넣어준다.
else {
nodes[i / 2].rightChild = &nodes[i];
}
}
cout<<"pre : ";
preorder(&nodes[1]);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"in : ";
inorder(&nodes[1]);
cout<<endl;
cout<<"post : ";
postorder(&nodes[1]);
return 0;
}트리 응용
- 전위 순회(pre order) 결과가 주어졌을때 트리 복원하기
- -1은 노드 끝을 의미합니다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int> pi;
vector<pi> tree[10000];
vector<int> restore;
int visit[10000];
stack<int> s;
void makeTree(int idx, int node, vector<int> &v) {
visit[idx] = 1;
//end node
if(v[idx] == -1) {
//left
if(tree[node][0].first == -2) {
tree[node][0].first = -1;
}
else { // right
tree[node][0].second = -1;
}
return;
}
//not to exist node
if(tree[v[idx]].empty()) {
s.push(v[idx]);
tree[v[idx]].push_back({-2,-2});
}
//exist node
if(tree[node][0].first == -2) {
tree[node][0].first = v[idx];
} else if(tree[node][0].second == -2) {
tree[node][0].second = v[idx];
}
makeTree(idx+1,v[idx],v);
}
void traversal(int node) {
if(node == -1) {
restore.push_back(-1);
return;
}
else if(node > 0) {
restore.push_back(node);
traversal(tree[node][0].first);
traversal(tree[node][0].second);
}
}
bool solve(vector<int> &v) {
int root = v[0];
if(root == -1) {
return true;
}
visit[0] = 1;
tree[root].push_back({-2,-2});
s.push(root);
int cur = root;
for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) {
if(!visit[i]) {
makeTree(i, cur, v);
if(!s.empty()) {
cur = s.top(); s.pop();
}
}
}
traversal(root);
for (int i = 1; i < v.size(); i++) {
if(restore.size()!=v.size()) return false;
if(restore[i]!=v[i]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main(void) {
vector<int> test1 = {-1};
vector<int> test2 = {3,5,6,8,-1,-1,-1,1,7,-1,-1,-1,4,-1,2,-1,-1};
vector<int> test3 = {1,-1,2,-1,-1,3,-1,-1};
cout << solve(test1) << "\n";
cout << solve(test2) << "\n";
cout << solve(test3) << "\n";
return 0;
}
트리 문제(BOJ)
코드(C++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
char data;
Node* left;
Node* right;
//생성자
Node(char data) {
this->data = data;
this->left = NULL;
this->right = NULL;
}
};
typedef struct Tree {
Node* root;
//생성자
Tree() {
root = NULL;
}
//노드 생성
void nodeInsert(char data, char left, char right) {
if(root == NULL) {
if(data != '.') root = new Node(data);
if(left != '.') root->left = new Node(left);
if(right != '.') root->right = new Node(right);
} else {
nodeSearch(root, data, left, right);
}
}
//노드 찾기
void nodeSearch(Node* root, char data, char left, char right) {
if(root == NULL) return;
else if(root->data == data) {
if(left != '.') root->left = new Node(left);
if(right != '.') root->right = new Node(right);
} else {
nodeSearch(root->left, data, left, right);
nodeSearch(root->right, data, left, right);
}
}
} Tree;
void pre(Node* root) {
cout << root->data;
if(root->left != NULL) pre(root->left);
if(root->right != NULL) pre(root->right);
}
void in(Node* root) {
if(root->left != NULL) in(root->left);
cout << root->data;
if(root->right != NULL) in(root->right);
}
void post(Node* root) {
if(root->left != NULL) post(root->left);
if(root->right != NULL) post(root->right);
cout << root->data;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
int n;
cin >> n;
Tree tree;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char data, left, right;
cin >> data >> left >> right;
tree.nodeInsert(data, left, right);
}
pre(tree.root);cout<<"\n";
in(tree.root);cout<<"\n";
post(tree.root);
return 0;
}코드(Java)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
class Node {
char data;
Node left, right;
public Node(char data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
class Tree {
Node root;
public void nodeInsert(char data, char left, char right) {
if(root == null) {
if(data != '.') root = new Node(data);
if(left != '.') root.left = new Node(left);
if(right != '.') root.right = new Node(right);
} else {
nodeSearch(root, data, left, right);
}
}
public void nodeSearch(Node root, char data, char left, char right) {
if(root == null) return;
else if(root.data == data) {
if(left != '.') root.left = new Node(left);
if(right != '.') root.right = new Node(right);
} else {
nodeSearch(root.left, data, left, right);
nodeSearch(root.right, data, left, right);
}
}
public void pre(Node root) {
System.out.print(root.data);
if(root.left != null) pre(root.left);
if(root.right != null) pre(root.right);
}
public void in(Node root) {
if(root.left != null) in(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data);
if(root.right != null) in(root.right);
}
public void post(Node root) {
if(root.left != null) post(root.left);
if(root.right != null) post(root.right);
System.out.print(root.data);
}
}
public class boj1991 {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(bf.readLine());
Tree tree = new Tree();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char str[] = bf.readLine().replace(" ", "").toCharArray();
tree.nodeInsert(str[0], str[1], str[2]);
}
tree.pre(tree.root);
System.out.println();
tree.in(tree.root);
System.out.println();
tree.post(tree.root);
System.out.println();
bf.close();
}
}코드(C++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void postOrder(string pre, string in) {
if(!pre.length()) return;
int n = pre.size();
char root = pre[0];
int left = find(in.begin(),in.end(),root) - in.begin();
int right = n - left - 1;
postOrder(pre.substr(1,left), in.substr(0,left));
postOrder(pre.substr(left+1,n), in.substr(left+1,n));
cout << root;
}
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
while (!cin.eof()) {
string in, pre;
cin >> pre >> in;
postOrder(pre, in);
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}코드(Java)
import java.util.*;
class Tree {
class Node {
char data;
Node left, right;
Node(char data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node root;
static int pIndex = 0;
public void buildTreeByInPre(char in[], char pre[]) {
pIndex = 0;
root = buildTreeByInPre(in, pre, 0, in.length - 1);
}
private Node buildTreeByInPre(char[] in, char[] pre, int start, int end) {
if(start > end) return null;
Node node = new Node(pre[pIndex++]);
if(start == end) return node;
int mid = search(in, start, end, node.data);
node.left = buildTreeByInPre(in, pre, start, mid-1);
node.right = buildTreeByInPre(in, pre, mid+1, end);
return node;
}
private int search(char[] in, int start, int end, char data) {
int i = 0;
for (i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if(in[i] == data) return i;
}
return i;
}
public void printInorder(Node node) {
if(node == null) return;
printInorder(node.left);
printInorder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(sc.hasNextLine()) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
String inpre[] = str.split(" ");
Tree tree = new Tree();
char pre[] = new char[inpre[0].length()];
char in[] = new char[inpre[1].length()];
for (int i = 0; i < inpre[0].length(); i++) {
pre[i] = inpre[0].charAt(i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < inpre[1].length(); i++) {
in[i] = inpre[1].charAt(i);
}
tree.buildTreeByInPre(in, pre);
tree.printInorder(tree.root);
System.out.print("\n");
}
sc.close();
}
}