힙 정렬(Heap Sort) 이란?
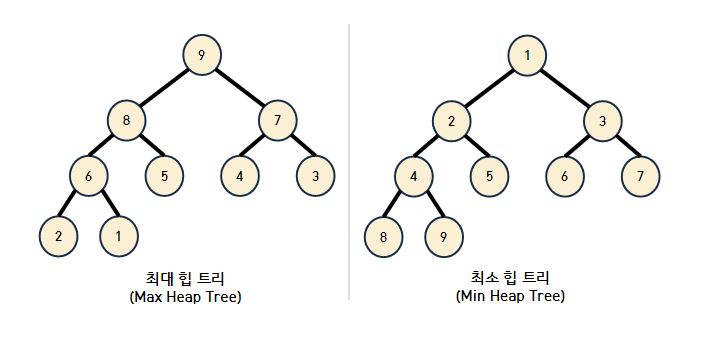
- 힙 정렬(Heap Sort) 이란 최대 힙 트리(내림차순 정렬) 나 최소 힙 트리(오름차순 정렬) 를 구성해 정렬을 하는 방법이다.
- 힙 정렬은 힙 트리 구조(Heap Tree Structure)를 이용하는 정렬 방법이다.
힙 정렬(Heap Sort) 알고리즘의 특징
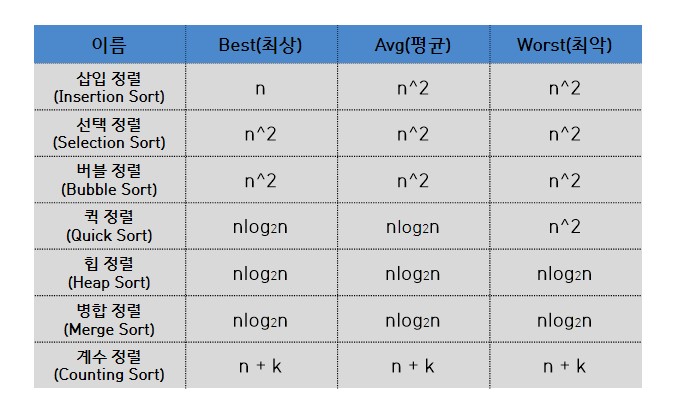
- 최악의 경우에도 시간 복잡도가 O(NlogN)이 되는 빠른 정렬 입니다.
- 힙 정렬은 추가 메모리 사용이 필요없는 in-place sort입니다.
- 힙 이라는 자료구조를 이용해서 정렬을 합니다.
- 힙(heap)은 최댓값, 최솟값을 찾아내는 연산을 빠르게 하기 위해 고안된 완전 이진 트리(complete binary tree) 을 기본으로 한 자료구조 입니다.
- 힙은 다음 힙 속성(property) 을 만족합니다.
- A가 B의 부모노드(parent node) 이면, A의 키(key)값과 B의 키값 사이에는 대소관계가 성립한다.
힙 정렬(Heap Sort)의 알고리즘 예시
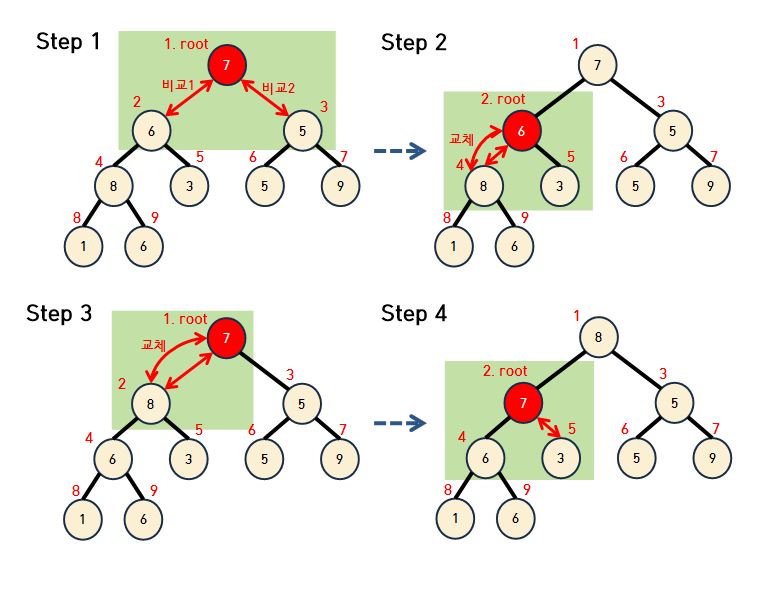
- 전체 트리 구조를 최대 힙 구조로 바꾼다.
- Step 1. 1번 노드(부모노드)는 2번, 3번(자식노드)과 비교한다. 만약 1번 노드가 2번 3번 보다 작다면 교체하고 부모노드 보다 값이 큰 자식노드가 없다면 다음 영역(연두색 상자)으로 넘어간다.
- Step 2. 2번 노드(6) 4번 노드(8) 자식노드가 부모노드보다 값이 크기 때문에 교체한다.
- Step 3. 1번 노드와 2번 노드 비교 후 교체한다.
- Step 4. 2번 노드와 5번 노드 비교한다.
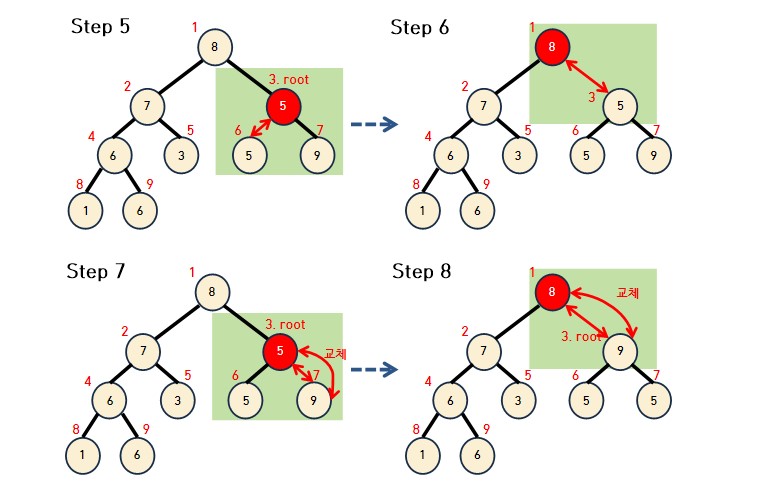
- Step 5. 3번과 6번 비교후 Step 6과 같이 3번 노드의 부모노드와 비교한다.
- Step 7, 8번도 동일하게 수행한다.
- for루프는 노드의 개수만큼만 수행한다.
- 아래의 소스의 결과로 최대 힙 구조로 변경이 된다.
힙 구조로 변경하는데 걸리는 시간 복잡도는 O(N * logN)이다.
// 전체 트리 구조를 최대 힙 구조로 바꾼다.
for(int i = 1; i < num; i++){
int c = i;
do {
// 특정 원소의 부모
int root = (c - 1) / 2;
if(heap[root] < heap[c]){
int tmp = heap[root];
heap[root] = heap[c];
heap[c] = tmp;
}
c = root;
for(int i=0; i < num; i++){
printf("%d ",heap[i]);
}
printf("\n");
} while (c != 0);
}
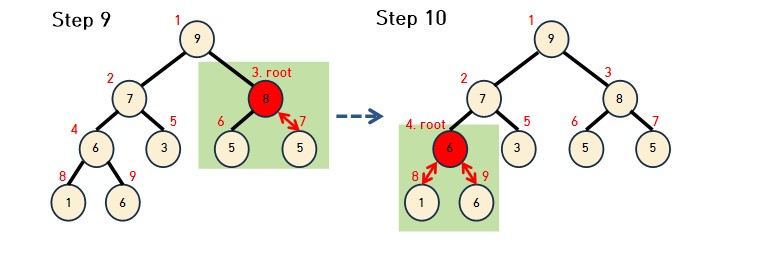
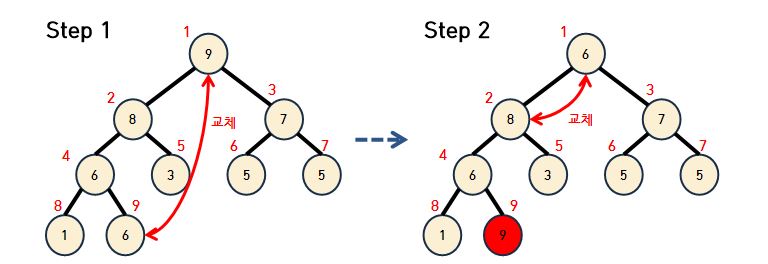
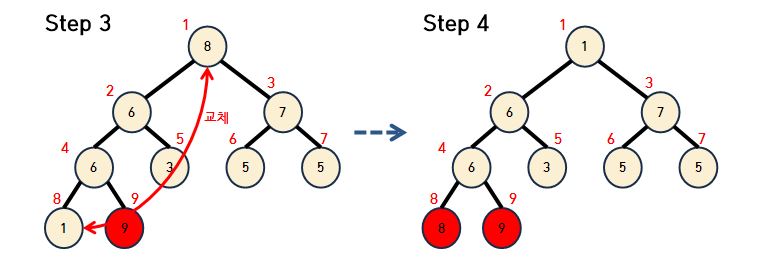
- 다음은 정렬을 수행 하는 과정이다. 루트노드를 맨 뒤쪽으로 보내면서 트리의 크기를 1개 씩 빼준다.
- 9와 6을 바꾼 뒤 9는 정렬이 완료 됬으므로 빨간색으로 칠한다.
- 루트의 8을 맨 뒷쪽의 원소와 교체하고 빨간색으로 칠하고 트리의 크기 1을 빼준다. 그리고 이 과정을 반복해 준다.
힙 정렬 구현하기
- C++ 예시1(최대 힙, 일반 구현법)
- C++ 예시2(최대 힙, 최소 힙, 빠른 구현법)
- Java 예시1(최대 힙, 최소 힙)
C++ 예시1(최대 힙, 일반 구현법)
#include <stdio.h>
int num = 9;
int heap[9] = {7, 6, 5, 8, 3, 5, 9, 1, 6};
int main(void){
// 전체 트리 구조를 최대 힙 구조로 바꾼다.
for(int i = 1; i < num; i++){
int c = i;
do {
// 특정 원소의 부모
int root = (c - 1) / 2;
if(heap[root] < heap[c]){
int tmp = heap[root];
heap[root] = heap[c];
heap[c] = tmp;
}
c = root;
for(int i=0; i < num; i++){
printf("%d ",heap[i]);
}
printf("\n");
} while (c != 0);
}
// 크기를 줄여가며 반복적으로 힙을 구성한다.
for(int i = num - 1; i >= 0; i--){
int tmp = heap[0];
heap[0] = heap[i];
heap[i] = tmp;
int root = 0;
int c = 1;
do {
c = 2 * root + 1;
// 자식 중에 더 큰 값을 찾기
if(heap[c] < heap[c+1] && c < i-1){
c++;
}
// 루트보다 자식이 더 크면 교환
if(heap[root] < heap[c] && c < i){
int tmp = heap[root];
heap[root] = heap[c];
heap[c] = tmp;
}
root = c;
} while (c < i);
}
printf("결과 \n");
// 결과 출력
for(int i=0; i < num; i++){
printf("%d ",heap[i]);
}
return 0;
}
C++ 구현예시2(최대 힙, 최소 힙, 빠른 구현법)
/*
* Max Heap
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int heap_size;
int heap[10001];
int max_push(int data) {
int target = heap_size + 1;
//루트노드가 data보다 작으면 자식노드로 복사
while (target != 1 && heap[target/2] < data) {
heap[target] = heap[target/2];
target /= 2;
}
heap[target] = data;
heap_size++;
}
void max_pop() {
int parent = 1, child = 2;
int last = heap[heap_size];
while (child < heap_size) {
//right 유무 && left가 right보다 작을때
if(child+1 < heap_size && heap[child] < heap[child+1]) {
child++;//큰 값 선택(right)
}
if(last >= heap[child]) {//마지막 노드가 자식 보다 크거나 같으면 종료
break;
}
//그렇지 않으면 자식 노드를 루트에 저장
heap[parent] = heap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
heap[parent] = last;
heap_size--;
}
void solve() {
//input
int arr[10] = {4,3,2,6,3,8,9,1,7,5};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
max_push(arr[i]);
}
//Max Heap Result
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
cout << heap[1] << " ";
max_pop();
}
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
solve();
return 0;
}
/*
* Min Heap
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int heap_size;
int heap[10001];
int min_push(int data) {
int target = heap_size + 1;
//루트노드가 data보다 크면 자식노드로 복사
while (target != 1 && heap[target/2] > data) {
heap[target] = heap[target/2];
target /= 2;
}
heap[target] = data;
heap_size++;
}
void min_pop() {
int parent = 1, child = 2;
int last = heap[heap_size];
while (child < heap_size) {
//right 유무 && left가 right보다 클때
if(child+1 < heap_size && heap[child] > heap[child+1]) {
child++;//작은 값 선택(right)
}
if(last <= heap[child]) {//마지막 노드와 자식노드 중 작은 값
break;
}
heap[parent] = heap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
heap[parent] = last;
heap_size--;
}
void solve() {
//input
int arr[10] = {4,3,2,6,3,8,9,1,7,5};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
min_push(arr[i]);
}
//Min Heap Result
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
cout << heap[1] << " ";
min_pop();
}
}
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
solve();
return 0;
}
Java 예시1(최대 힙, 최소 힙)
class Main {
static int[] maxHeap = new int[10001];
static int maxHeapSize;
static int[] minHeap = new int[10001];
static int minHeapSize;
/*
* Max Heap
*/
public static void maxPush(int data) {
int target = maxHeapSize + 1;
while(target != 1 && maxHeap[target/2] < data){
maxHeap[target] = maxHeap[target/2];
target /= 2;
}
maxHeap[target] = data;
maxHeapSize++;
}
public static void maxPop() {
int parent = 1, child = 2;
int last = maxHeap[maxHeapSize];
while(child < maxHeapSize) {
if(child+1 < maxHeapSize && maxHeap[child] < maxHeap[child+1]) {
child++;
}
if(last >= maxHeap[child]) break;
maxHeap[parent] = maxHeap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
maxHeap[parent] = last;
maxHeapSize--;
}
/*
* Min Heap
*/
public static void minPush(int data) {
int target = minHeapSize + 1;
while(target != 1 && minHeap[target/2] > data){
minHeap[target] = minHeap[target/2];
target /= 2;
}
minHeap[target] = data;
minHeapSize++;
}
public static void minPop() {
int parent = 1, child = 2;
int last = minHeap[minHeapSize];
while(child < minHeapSize) {
if(child+1 < minHeapSize && minHeap[child] > minHeap[child+1]) {
child++;
}
if(last <= minHeap[child]) break;
minHeap[parent] = minHeap[child];
parent = child;
child *= 2;
}
minHeap[parent] = last;
minHeapSize--;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//input
int[] data = {2,3,7,4,5,1,9,4,8,6};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
maxPush(data[i]);
minPush(data[i]);
}
//result
System.out.println("===Max Heap===");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.print(maxHeap[1]+" ");
maxPop();
}
System.out.println("\n===Min Heap===");
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.print(minHeap[1]+" ");
minPop();
}
}
}
힙 정렬(Heap Sort)의 시간복잡도
힙 정렬의 시간복잡도는 O(N*logN) 이다.