큐(Queue) 란?
자료의 입력과 출력을 한 쪽 끝(front, rear)으로 제한한 자료구조
FIFO(First In First Out) 먼저 들어온 것이 먼저 나가는 자료 구조일상생활을 예로 들면 은행에서 먼저 들어온 사람이 먼저 창구나 입장을 하는 것과 같다고 보면 된다.
큐(Queue)의 용도
컴퓨터 버퍼 에서 주로 사용한다.
서비스의 순서를 기다리는 등 대기행렬의 업무처리
운영체제의 작업 스케줄링
큐(Queue)의 특징
큐 선형구조 이다.
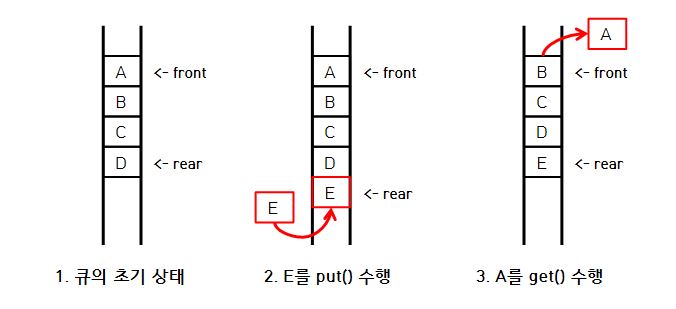
FIFO(First In First Out) 선입선출 구조이다.put(): 자료를 넣을때 수행하는 연산 rear 포인터가 가리킨다.get(): 자료를 삭제할때 수행하는 연산 front 포인터가 가리킨다.단점
큐에 빈 메모리가 남아 있어도 꽉 차있는것으로 판단할 수 있다.(rear가 배열의 끝에 도달했을 경우)원형 큐가 나옴
원형 큐는 메모리 공간은 잘 활용하나 배열로 구현되어 있기 때문에 큐의 크기가 제한된다.링크드 리스트로 큐가 나옴링크드 리스트로 구현한 큐는 큐의 크기가 제한이 없고 삽입, 삭제가 편리하다.
큐(Queue)의 성질
FIFO(First In First Out) 원소의 추가가 O(1)
원소의 제거가 O(1)
제일 앞/뒤의 원소 확인이 O(1)
제일 앞/뒤가 아닌 나머지 원소들의 확인/변경이 원칙적으로 불가능
선형구조 의 자료구조이다.
큐(Queue)의 알고리즘 예시
C 언어를 이용한 Queue 구현
# include < stdio . h >
# include < stdlib . h >
typedef struct Node {
int data ;
Node * next ;
} Node ;
typedef struct Queue {
Node * front ;
Node * rear ;
int len ;
} Queue ;
void put ( Queue * q , int data ) {
Node * node = ( Node * ) malloc ( sizeof ( Node ));
node -> data = data ;
node -> next = q -> rear ;
if ( q -> len == 0 ) {
q -> front = q -> rear = node ;
} else {
q -> rear -> next = node ;
q -> rear = q -> rear -> next ;
}
q -> len ++ ;
}
int get ( Queue * q ) {
if ( q -> front == NULL ) {
printf ( " UnderFlow \n " );
return - 1 ;
}
Node * node = q -> front ;
int data = node -> data ;
q -> front = node -> next ;
free ( node );
q -> len -- ;
return data ;
}
void show ( Queue * q ) {
printf ( " \n ----show---- \n " );
int lentmp = q -> len ;
Node * node = q -> front ;
while ( lentmp > 0 ) {
printf ( " %d " , node -> data );
node = node -> next ;
lentmp -- ;
}
}
int main ( void ) {
Queue q ;
q . front = NULL ;
q . rear = NULL ;
q . len = 0 ;
put ( & q , 1 );
put ( & q , 2 );
put ( & q , 3 );
put ( & q , 4 );
show ( & q );
get ( & q );
show ( & q );
return 0 ;
} Java 언어를 이용한 Queue 구현
public class myqueue {
public static class Node {
private Object data ;
private Node next ;
public Node ( Object data ) {
this . data = data ;
this . next = null ;
}
}
private Node front ;
private Node rear ;
int len = 0 ;
public void put ( Object data ) {
Node node = new Node ( data );
if ( len == 0 ) {
front = node ;
rear = node ;
} else {
rear . next = node ;
rear = rear . next ;
}
len ++ ;
}
public Object get () {
if ( front == null ) {
System . out . println ( " UnderFlow " );
return - 1 ;
}
Object data = front . data ;
front = front . next ;
return data ;
}
public Object peak () {
Object data = front . data ;
return data ;
}
public void show () {
System . out . println ( " ----show---- " );
Node node = front ;
while ( node != null ) {
System . out . println ( node . data );
node = node . next ;
}
}
} C++ 배열을 이용한 큐 구현
// #include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std ;
#define ll long long
const int mx = 1000005 ;
int dat [ mx ];
int head = 0 , tail = 0 ;
void push ( int x ) {
dat [ tail ++ ] = x ;
}
void pop () {
head ++ ;
}
int front () {
return dat [ head ];
}
int back () {
return dat [ tail - 1 ];
}
int main () {
cin . tie ( nullptr );
ios :: sync_with_stdio ( false );
push ( 1 );
push ( 2 );
push ( 3 );
cout << front ();
return 0 ;
}
C++ STL Library를 사용한 Queue 구현
# include < iostream >
# include < queue >
using namespace std ;
int main ( void ){
queue < int > q ;
q . push ( 8 );
q . push ( 7 );
q . push ( 6 );
q . pop ();
q . push ( 5 );
q . pop ();
while ( ! q . empty ()){
cout << q . front () << ' ' ;
q . pop ();
}
return 0 ;
} References
Please enable JavaScript to view the
comments powered by Disqus.