[Boj] 14499.주사위 굴리기
by me
14499.주사위 굴리기 문제 출처 14499.주사위 굴리기 - 문제 링크이 곳 입니다.
- n: 지도의 열(colunm)
- m: 지도의 행(row)
- x: 주사위 행 번호 (중요***********)
- y: 주사위 열 번호 (중요***********)
- k: 명령어 개수(동:1,서:2,남:3,북:4)
접근 방법
- 지도에 x,y 위치에 주사위가 놓여있을때 1번째 명령어 수행했을때 범위를 벗어나는지 확인한다.
- 벗어난다면 아무것도 하지말고 pass
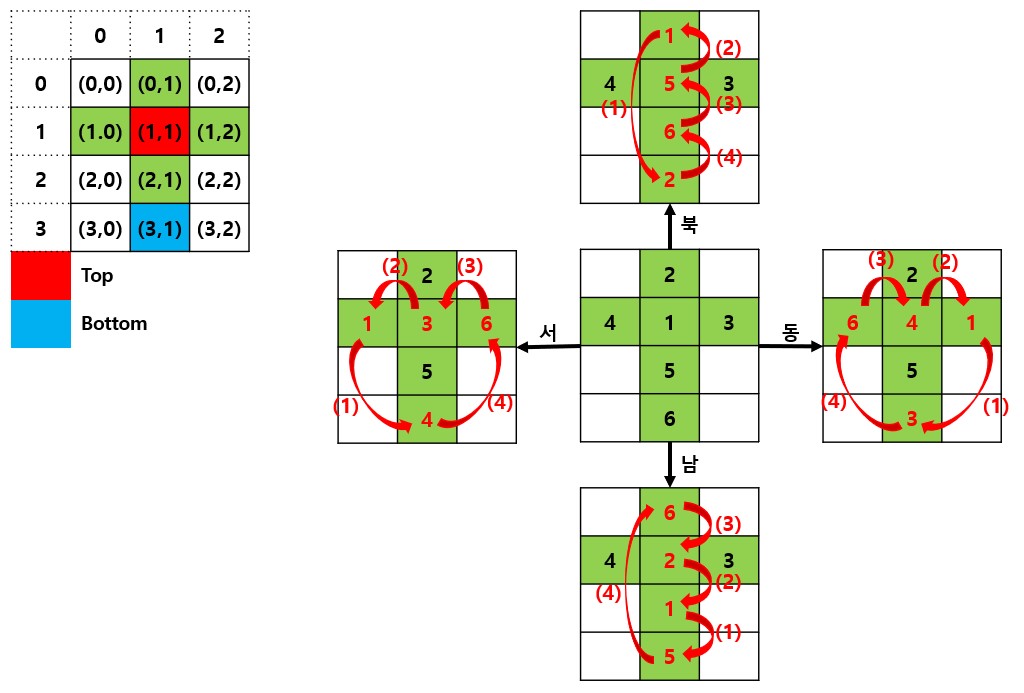
- 범위 안쪽이라면 주사위를 명령어 방향으로 1회 굴린다.(주사위 굴리는 방법은 아래 사진 참고)
- 주사위를 굴렸을때 지도의 값이 0이라면 주사위 바닥의 값을 지도에 복사
- 주사위를 굴렸을때 지도의 값이 0이 아니라면 지도의 값을 주사위 바닥에 복사하고 지도의 값은 0으로 저장
- 그리고 주사위 윗쪽(top)의 깂 출력한다.
주사위 굴릴때 변화
void diceMove(int d) {
int tmp;
switch (d) {
case 1://동
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[1][2];
dice[1][2] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[1][0];
dice[1][0] = tmp;
break;
case 2://서
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[1][0];
dice[1][0] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[1][2];
dice[1][2] = tmp;
break;
case 3://북
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[0][1];
dice[0][1] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[2][1];
dice[2][1] = tmp;
break;
case 4://남
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[2][1];
dice[2][1] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[0][1];
dice[0][1] = tmp;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
소스코드(C++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
int n, m, x, y, k;
int dice[4][3] = {
{0,0,0},
{0,0,0},
{0,0,0},
{0,0,0}
};
int moveX[5] = {0,0,0,-1,1};
int moveY[5] = {0,1,-1,0,0};
vector<vector<int> > mymap;
vector<int> command;
void diceMove(int d) {
int tmp;
switch (d) {
case 1://동
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[1][2];
dice[1][2] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[1][0];
dice[1][0] = tmp;
break;
case 2://서
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[1][0];
dice[1][0] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[1][2];
dice[1][2] = tmp;
break;
case 3://북
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[0][1];
dice[0][1] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[2][1];
dice[2][1] = tmp;
break;
case 4://남
tmp = dice[3][1];//bottom
dice[3][1] = dice[2][1];
dice[2][1] = dice[1][1];
dice[1][1] = dice[0][1];
dice[0][1] = tmp;
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void solve(int r, int c) {
for (int i = 0; i < command.size(); i++) {
int move = command[i];
int nx = moveX[move];
int ny = moveY[move];
if(r+ny >= 0 && c+nx >= 0 && r+ny < m && c+nx < n) {
c += nx;
r += ny;
diceMove(move);
if(mymap[c][r] == 0) {
mymap[c][r] = dice[3][1];
} else {
dice[3][1] = mymap[c][r];
mymap[c][r] = 0;
}
cout << dice[1][1] << "\n";
}
}
}
int main() {
cin.tie(nullptr);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin >> n >> m >> y >> x >> k;
mymap.assign(n, vector<int>(m, 0));
command.assign(k,0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
cin >> mymap[i][j];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){
cin >> command[i];
}
solve(x, y);
return 0;
}